TANKA'S
TECHNICAL
BULLETIN
IN A NUTSHELL
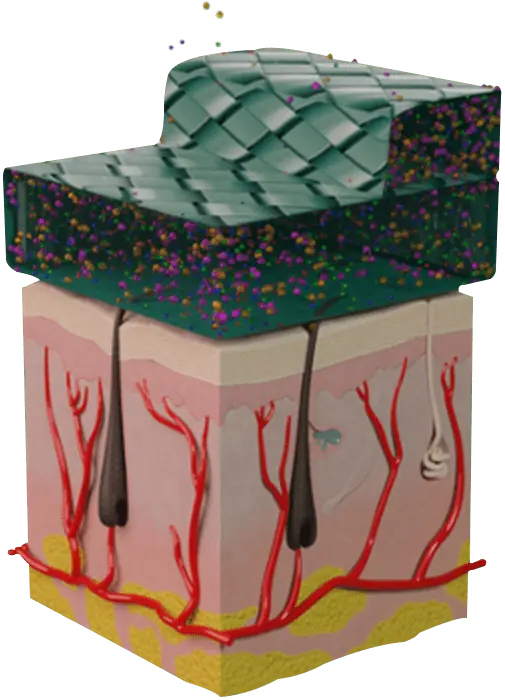
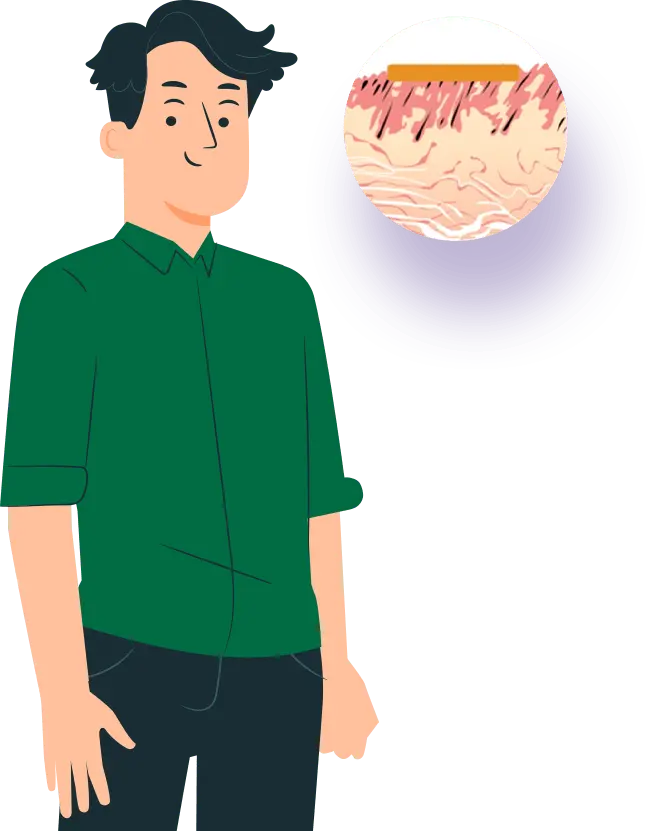
Schematic representation of transdermal drug delivery mechanisms
The skin is a potential site for active ingredients’ administration via absorption, due to the large surface area of this organ.
However, the absorption of chosen ingredients such as dietary supplements throughout the skin is very challenging, because there is the first barrier that must be passed, the SC [stratum corneum].
For administered active ingredients to be absorbed into the circulation, they must first permeate into the skin via this molecular architecture.
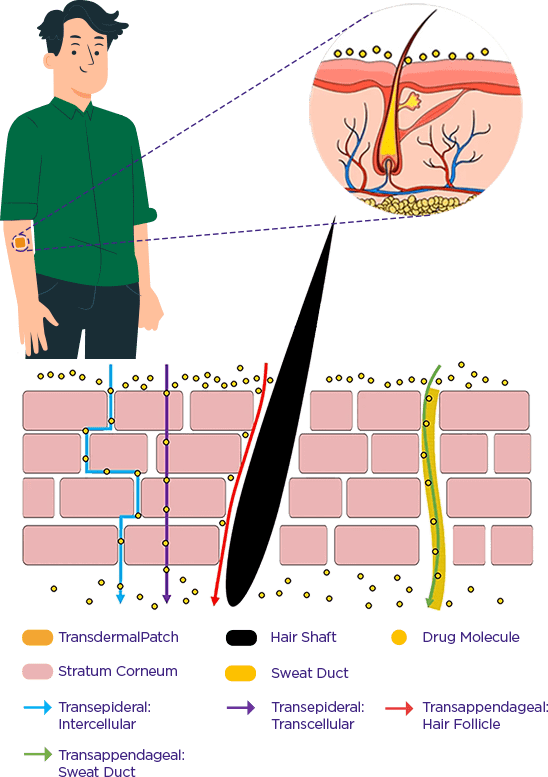
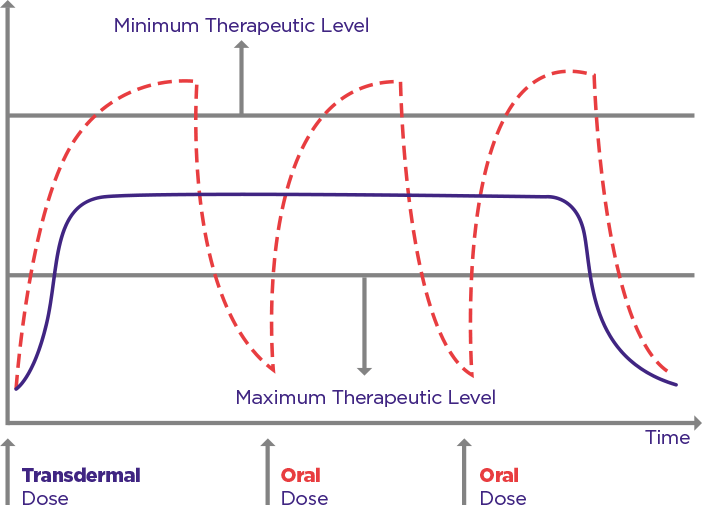
Tanaka’s way of transdermal intake of dietary supplements bypass first pass metabolism, wear & forget for up to 30 days, ease-of-use, achieves long-lasting, consistent administration, which ensures stable, and an efficient outcome as well as oral administration with large amounts of active ingredients due to a steadily available therapeutic concentration.
Reference: Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems: current trends and applications.
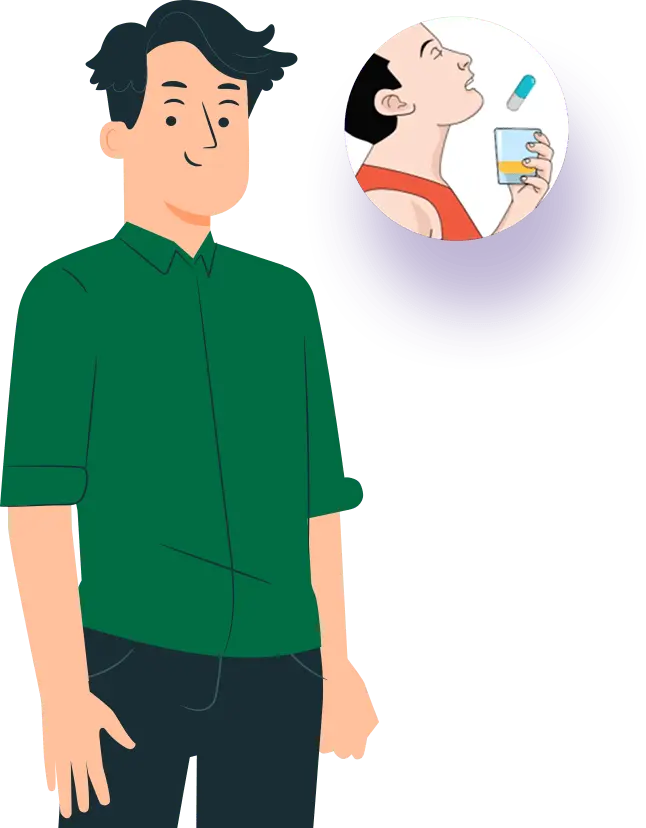

COMPARISON OF THREE DIFFERENT ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION:
oral, intravenous injection and transdermal
ADVANTAGES
- Avoid Pain
- Easy to Swallow and Convenient
- Various Dosages Forms
- Self-Administration
- High Patient Compliance
DISADVANTAGES
- Enzymatic Degradation
- Acidic Environment in GIT
- Longer Absortion Process
- Plasma Level Slowly Achieved
- First Pas Metabolism
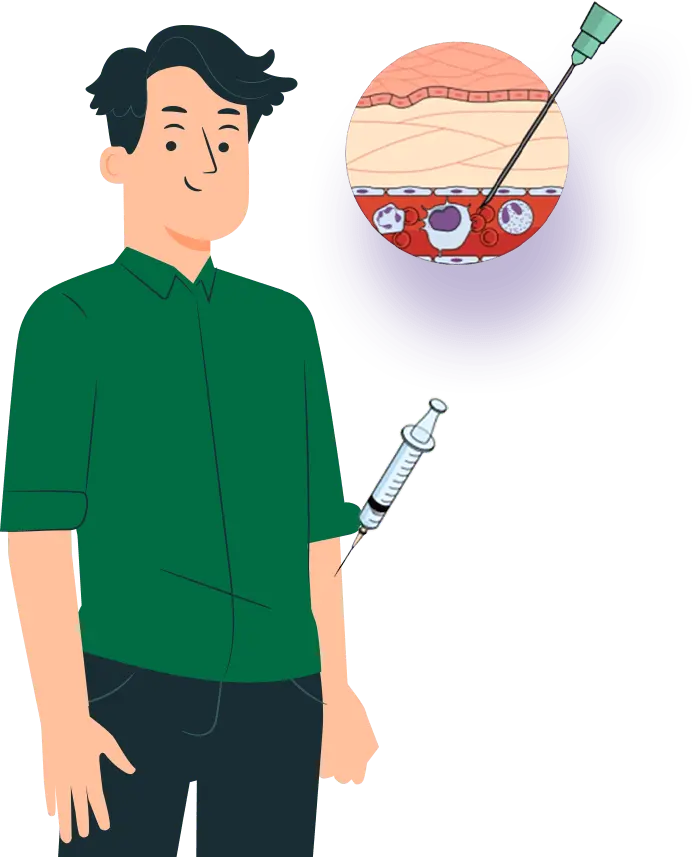
COMPARISON OF THREE DIFFERENT ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION:
oral, intravenous injection and transdermal
ADVANTAGES
- 100% Bioavailability
- Plasma Level can be Achieved Quickly
- Avoid Hepatic Metabolism
- Used in Emergency Condition
- Accurate Dose
DISADVANTAGES
- Invasive
- Painful
- Expert Personnel Needed
- No Self-Administration
- Needles Waste Disposal Problems
COMPARISON OF THREE DIFFERENT ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION:
oral, intravenous injection and transdermal
ADVANTAGES
- Not or Less Invasive
- Ease on Application
- Self-Administration
- First Pass Metabolism Avoidance
- Various Dosage Forms and Methods
- May Reduce the Frequency of Administration
DISADVANTAGES
- May Cause Skin Irritation at the Application Site
- Limited to Suitable Drugs
- Plasma Level may be Achieved Slowly